Understanding Calf Blood Clot Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide

When it comes to our health, awareness is key. Many individuals may experience calf blood clot symptoms without even being aware of what they represent. This article aims to delve deep into the nature of these symptoms, the underlying causes of blood clots, and effective prevention and treatment strategies. If you seek to enhance your understanding of vascular health, particularly regarding calf blood clots, you are in the right place.
What is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot is a mass of blood components that clump together to stop bleeding. While this process is vital for healing, clots can sometimes form inappropriately, leading to serious medical conditions. When a blood clot forms in the veins of the leg, it is often referred to as Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), which can potentially lead to severe complications such as a pulmonary embolism if the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs.
Recognizing Calf Blood Clot Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of a calf blood clot is essential for mitigating health risks. Common calf blood clot symptoms include:
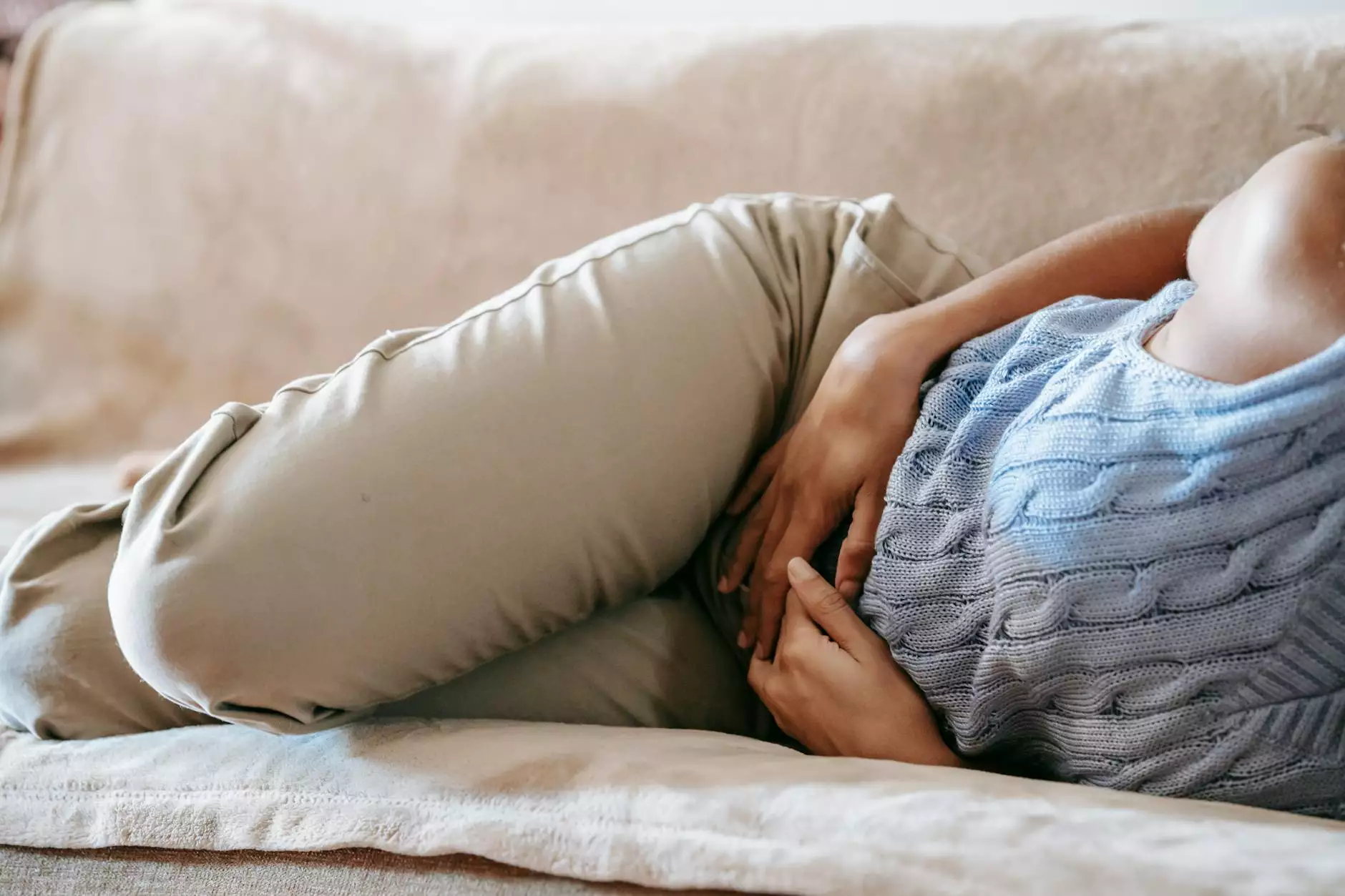
- Swelling in one leg or calf, which may feel warmer to the touch.
- Pain or tenderness in the calf, often described as a cramp or soreness that may worsen when standing or walking.
- Skin discoloration, possibly turning blue or a darker shade than the unaffected leg.
- Enlargement of the veins near the surface of the skin.
It is crucial to note that not everyone with a clot will exhibit obvious symptoms. Some individuals may be asymptomatic, which is why awareness and preventive measures are paramount.
The Causes of Blood Clots in the Calf
Understanding the underlying causes of calf blood clots is vital to prevention. The most prevalent factors contributing to clot formation include:
- Immobility: Long periods of inactivity, such as extended travel or bed rest, can lead to stagnant blood flow.
- Injury: Trauma to the leg can result in blood vessel damage, increasing the risk of clotting.
- Pill usage: Hormonal medications like birth control can increase the chance of developing blood clots.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional pressure on blood vessels, inhibiting healthy circulation.
- Family history: Genetic predispositions can make some individuals more susceptible to clot formation.
Preventing Calf Blood Clots
Preventing calf blood clots involves proactive measures. Here’s how you can reduce your risk:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity promotes healthy blood circulation. Aim to incorporate both aerobic exercises and strength training.
- Wear Compression Stockings: Graduated compression stockings can enhance blood flow in the legs, particularly during long periods of sitting or standing.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can thicken the blood, making clots more likely. Drink plenty of fluids, especially during travel.
- Limit Prolonged Inactivity: If you’re traveling long distances, take breaks to stretch and walk around to encourage circulation.
- Consider Medications: For individuals at high risk, a doctor may prescribe anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent clot formation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Prompt medical attention is crucial for anyone experiencing the symptoms of a calf blood clot. If you notice any of the signs mentioned earlier, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Remember, timely intervention can save lives.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots in the Calf
Once you present the symptoms to a doctor, they will likely recommend a series of diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of a blood clot. These may include:
- Ultrasound: The most common procedure utilized to visualize blood flow in the veins of the leg.
- D-dimer Test: A blood test that measures the presence of a substance released when a blood clot breaks up.
- CT or MRI Scans: Imaging tests that offer detailed visuals of blood vessels in the affected area.
Treatment Options for Calf Blood Clots
Upon a diagnosis of a calf blood clot, the treatment approach will generally depend on the clot's size and location. Commonly recommended treatment options include:
- Anticoagulants: Medications that thin the blood and help dissolve clots.
- Thrombolytics: Powerful medications that dissolve clots quickly and are usually reserved for severe cases.
- Compression Therapy: Usage of compression stockings as mentioned before can aid recovery and minimize swelling.
- Surgery: In rare cases where medication is ineffective, surgical procedures may be necessary to remove a clot.
Living with and Managing Blood Clots
For many, a diagnosis of a blood clot will necessitate ongoing management to prevent recurrence. Here are key strategies:
- Regular Follow-ups: Regular consultations with a healthcare provider are essential in monitoring your condition.
- Adhering to Medication: Follow prescribed medication schedules diligently to prevent future clots.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Incorporate nutritious foods, stay physically active, and maintain a healthy weight.
Conclusion
Understanding calf blood clot symptoms can empower individuals to take charge of their vascular health. By recognizing early signs, understanding risk factors, and implementing preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of serious health issues related to blood clots. If you have any signs of a potential blood clot or are concerned about your vascular health, please consult with professionals at Truffles Vein Specialists. Your health is paramount, and early intervention can make a world of difference.